
CNC Wood Router Spindle Maintenance Guide: Ensuring Peak Performance
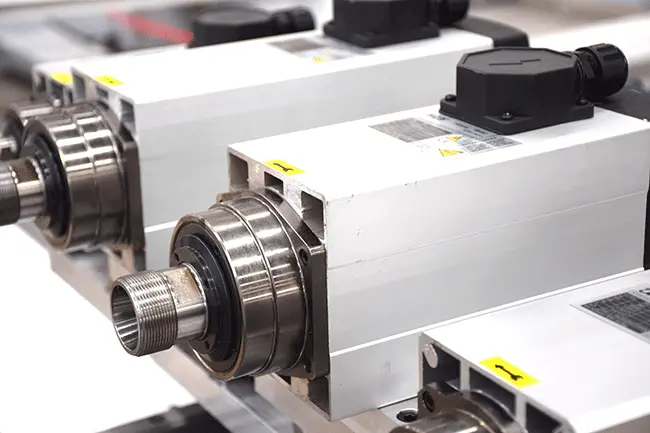
The spindle is the core of your CNC wood router, directly influencing machining accuracy, efficiency, and the machine’s lifespan. Proper spindle maintenance is crucial for stable operation and extending the longevity of your woodworking equipment. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of daily and periodic spindle maintenance procedures and important considerations for CNC wood router spindles, helping users like you maintain your machinery effectively and boost productivity.

1. Daily Care (After Each Use)
Consistent daily care is fundamental to keeping your spindle in top condition. Perform these steps after every use as part of your regular spindle maintenance routine.
1.1. Cleaning the Spindle Exterior
- Wipe down the spindle surface with a soft, lint-free cloth to remove dust, sawdust, and other debris. This simple step is essential for effective spindle maintenance.
- For stubborn marks, use a small amount of specialized, non-corrosive cleaning solution. Ensure the cleaner is safe for your spindle’s materials.
- Avoid using compressed air to blow directly into the spindle, as this can force contaminants into sensitive internal components like bearings. This precaution is important for proper spindle maintenance.
1.2. Cooling System Inspection
- Air-Cooled Spindles: Verify the cooling fan is operating correctly and that the cooling fins or channels are clear of obstructions. Clean any dust buildup from the fan blades and cooling pathways. Ensure adequate airflow around the spindle to prevent overheating, a key aspect of spindle maintenance.
- Liquid-Cooled Spindles: Check the coolant level in the reservoir and replenish as needed.
- Confirm that the coolant is circulating freely and the pump is functioning properly.
- Regularly replace the coolant to prevent scale and particle buildup in the cooling lines. Depending on usage and water quality, a weekly or monthly change is generally recommended as part of your spindle maintenance schedule.
- Inspect coolant hoses for any leaks and address them promptly.
- In colder climates, use appropriate antifreeze to prevent freezing and potential spindle damage.
1.3. Tool Holder and Tool Inspection
- Ensure the tool holder is securely fastened in the spindle collet. This is a critical safety and performance aspect of spindle maintenance.
- Check your cutting tools for any signs of looseness or damage and replace them immediately if necessary.
- Periodically clean both the tool holder shank and the spindle collet to remove dust and oxidation, ensuring good contact for optimal performance. This contributes to effective spindle maintenance.
1.4. Monitoring Spindle Sounds
- After the spindle has stopped, gently rotate it by hand and feel for any unusual resistance or grinding noises. This is a simple yet effective way to identify potential spindle maintenance needs.
- While the spindle is running at low speed, listen carefully for any abnormal friction sounds or vibrations. If you notice anything out of the ordinary, stop the machine and investigate the issue. Early detection is key in spindle maintenance.
2. Weekly Maintenance
Weekly maintenance builds upon daily care to ensure continued optimal performance and contributes significantly to long-term spindle maintenance.
2.1. Spindle Bearing Lubrication (For Applicable Models)
- Not all CNC wood router spindles require manual lubrication. Some advanced spindles feature sealed or automatic lubrication systems. Always consult your machine’s manual to determine if your spindle needs manual lubrication and the specific lubrication requirements. Understanding your specific model is crucial for proper spindle maintenance.
- If manual lubrication is required, use only the high-speed bearing grease recommended by the manufacturer.
- Following the manual’s instructions, use a professional grease gun to inject the correct amount of lubricant into the designated grease fittings. Correct lubrication is vital for effective spindle maintenance.
- Be mindful of the grease quantity; over-lubrication can lead to bearing overheating.
2.2. Spindle Motor Wiring Check
- Inspect the connections of the spindle motor’s power cables, control wires, and grounding wires to ensure they are secure and show no signs of loosening or damage. This electrical check is part of comprehensive spindle maintenance.
- Check the insulation of all wiring for any cracks or wear to prevent electrical hazards.
2.3. Spindle Motor Cleaning
- Use a soft brush or a vacuum cleaner with a brush attachment to remove dust from the surface of the spindle motor, promoting proper heat dissipation. This cleaning helps maintain optimal spindle status.
3. Monthly Maintenance Spindle
Monthly maintenance involves a more thorough examination and upkeep of the spindle, contributing to proactive spindle maintenance.
3.1. Checking Spindle Runout
- Use a precision dial indicator to measure both the radial and axial runout of the spindle. Monitoring runout is a critical aspect of spindle maintenance.
- If the runout exceeds the manufacturer’s specified tolerances, it may indicate worn or damaged spindle bearings, necessitating timely repair or replacement. Addressing runout issues is essential for proper maintenance.
3.2. Inspecting the Spindle Drawbar Mechanism
- Verify that the pneumatic or hydraulic drawbar system is functioning correctly, providing reliable clamping and release of the tool holder. Ensuring proper drawbar function is important
- Inspect the seals of the drawbar mechanism for any signs of damage or leakage.
3.3. Liquid Cooling System Maintenance (For Liquid-Cooled Spindles)
- Completely drain and replace the coolant. Clean the coolant tank and hoses to remove any accumulated scale or debris. Regular coolant replacement is a key part of maintenance for liquid-cooled systems.
- Check the performance of the coolant pump, ensuring it delivers the required flow rate and pressure.
3.4. Tightening Spindle Mounting Bolts
- Inspect the bolts that secure the spindle to the router frame and tighten them as needed to maintain proper alignment and stability. This mechanical check is part of thorough spindle maintenance.
4. Long-Term Spindle Care and Important Notes
- Avoid Prolonged Overloading: Operate the spindle within the specified technical parameters and processing guidelines for your machine. Avoid running at excessively high speeds or under heavy loads for extended periods. This helps prolong the life of your spindle and reduces the need for extensive spindle maintenance.
- Prevent Impacts: Exercise caution during operation to prevent the cutting tool or workpiece from colliding with the spindle, as this can cause significant damage. Preventing impacts is a crucial aspect of responsible maintenance.
- Schedule Regular Professional Service: Depending on your machine’s usage, arrange for professional maintenance of the spindle every six to twelve months. This may include bearing replacement, dynamic balancing, and other specialized procedures. Professional servicing is a vital component of comprehensive spindle maintenance.
- Maintain a Maintenance Log: Keep a detailed record of all spindle maintenance activities, including dates, tasks performed, and any issues encountered. This helps track the spindle’s performance and identify potential problems early.
- Adhere to the Machine Manual: Always consult and follow the specific instructions and recommendations provided in your CNC wood router’s manual. Different brands and models may have unique spindle designs and requirements.
5. Common Spindle Issues and Troubleshooting
Understanding common issues is helpful for effective spindle maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Spindle Getting Hot:
- Verify the proper functioning of the cooling system.
- Check for insufficient lubrication or damage to the spindle bearings.
- Ensure the spindle is not being overloaded.
- Confirm adequate ventilation around the machine.
- Unusual Spindle Noises:
- Check for loose or damaged cutting tools.
- Inspect the spindle bearings for signs of wear or damage.
- Check for any foreign objects inside the spindle housing.
- Reduced Machining Accuracy:
- Check the spindle runout to ensure it’s within acceptable limits.
- Inspect your cutting tools for wear or damage.
- Verify that the workpiece is securely clamped.
Conclusion
Proper spindle maintenance of your CNC wood router is paramount for ensuring efficient and reliable operation. By diligently following these daily, weekly, and monthly maintenance procedures, along with paying attention to long-term care and addressing common issues, you can significantly extend the life of your spindle, improve machining precision, and maximize your production output.If you have more questions, please contact us
Related Products
HALOONG CNC Cylindrical Shaft Polishing Machine
Dual Station Table Linear ATC CNC Wood Router: Automatic Tool Changer Wood CNC for Furniture Making
Why the HALOONG 12-Tool ATC CNC Wood Router Stands Out
The HALOONG 12-Tool ATC CNC Wood Router is a high-performance wood CNC machine built for exceptional efficiency and flexibility. Its automatic tool changer (ATC) switches between 12 tools in under 5 seconds, drastically reducing downtime and boosting output. Whether you’re cutting MDF, carving solid wood, or crafting intricate designs, this CNC wood router handles it all with ease. For even greater productivity, consider our optional dual-table configuration, which allows for near-continuous operation and significantly increases throughput for demanding production schedules.
Key Features of This CNC Wood Router
Here’s what makes this wood CNC a must-have:
Ultra-Fast Tool Switching
- 12-tool linear magazine: Holds a variety of tools, ready for instant use.
- Tool changes in under 5 seconds: The gantry-integrated design cuts travel time, keeping your production moving.
Versatile Material Processing
- Works with MDF, solid wood, OSB, PVC, acrylic, aluminum, and composite panels.
- Supports standard furniture joints (e.g., dowels and cams) and modern invisible connectors (e.g., Lamello, Peanut, Lockdowel).
- Perfect for cabinets, wardrobes, doors, and artistic carvings.
Customizable Worktable Options
- Options like 4'x8' (1220x2440 mm), 4'x9' (1220x2800 mm), or custom sizes available for single-table models.
- Maximize your output with our optional dual-table configuration, allowing for continuous loading and unloading on separate work zones.
- Upgraded vacuum table locks materials securely for flawless results on both single and dual-table setups.
Effortless Operation
- User-friendly controls with a clear display, network, and USB connectivity.
- Simplified design means even beginners can master it quickly. The dual-table operation is also intuitively managed through the advanced control system.
Built to Last with Precision
- Heavy-duty steel frame and high-precision gearbox for durability.
- Servo-driven system ensures smooth, accurate cuts every time. The robust construction ensures stability even during continuous operation on the dual-table model.
Cleaner, Safer Workspace
- Integrated dust collection and air-blow system keeps debris in check.
- Ideal for continuous, high-output runs without mess, making it perfect for the increased production demands of the dual-table system.
Top-Notch Support
- Free technical support, lifetime service, and remote assistance included.
PUR Glue Machine Kit For Edge Bander
Four-Spindle Dual-Station CNC Wood Router for Panel Furniture Manufactured
Maximize your panel furniture manufacturing throughput with the HALOONG Four-Spindle Dual-Station CNC Router. Expanding on the reliability of our single-station four-spindle CNC wood cutting machines, this dual-station system provides a substantial increase in production efficiency. It's designed for continuous operation, minimizing downtime and maximizing output through its smart workflow.
The clever dual-station workbench facilitates seamless alternating work cycles. While one station is engaged in machining, the operator can efficiently prepare the next batch of materials on the adjacent station. Upon completion of the first cycle, the machine instantly transitions to the pre-loaded second station. This continuous processing approach ensures no wasted time, making it a key asset for high-volume furniture production.








